Stroke is a serious medical condition that occurs when the blood supply to part of the brain is interrupted or reduced, depriving brain tissue of oxygen and nutrients. It is a leading cause of long-term disability and mortality worldwide. However, stroke prevention is possible through lifestyle changes and management of risk factors. Understanding the risk factors and adopting preventative measures are crucial steps in reducing the incidence of stroke and improving overall health and well-being.
Identifying Risk Factors
Several risk factors contribute to the development of stroke. Some factors such as age, gender, and family history cannot be changed. However, many factors are modifiable through lifestyle changes and medical interventions. Common risk factors include:
- High Blood Pressure (Hypertension): Hypertension is the single most important modifiable risk factor for stroke. Elevated blood pressure damages blood vessels over time, increasing the risk of stroke and other cardiovascular diseases.
- Diabetes: Uncontrolled diabetes can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of stroke. Managing blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication can help reduce this risk.
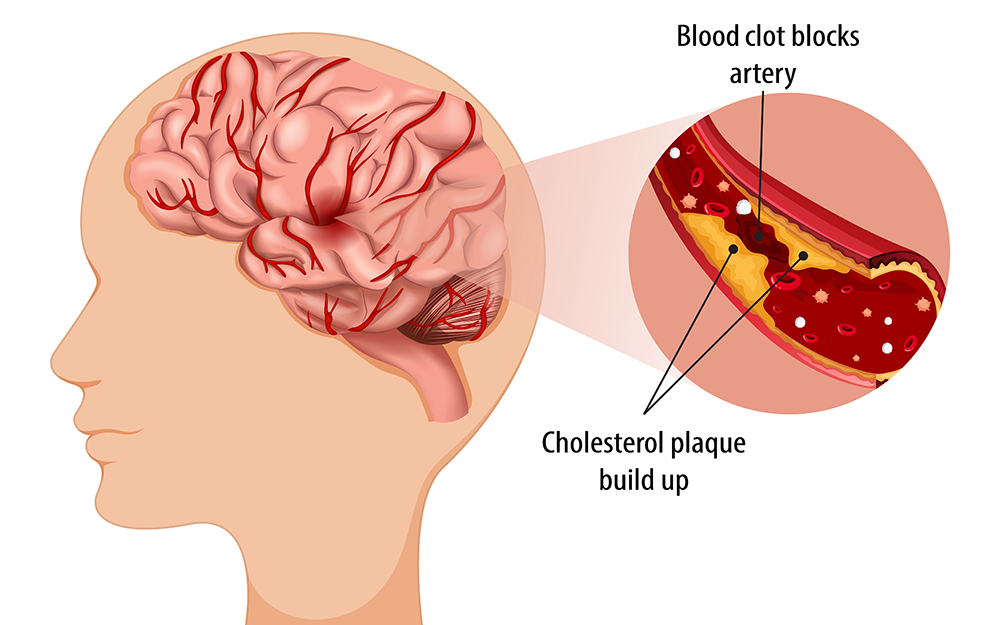
- High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of cholesterol can lead to the formation of plaque in the arteries, narrowing blood vessels and reducing blood flow to the brain. Maintaining cholesterol levels through diet, exercise, and medication when necessary is essential for stroke prevention.
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking damages blood vessels and increases the risk of blood clots, making smokers more susceptible to stroke. Quitting smoking significantly reduces this risk.
- Obesity and Physical Activity: Being overweight and leading a sedentary lifestyle are associated with a higher risk of stroke. Regular physical activity and a healthy diet can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of stroke.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Heavy alcohol consumption can raise blood pressure and contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases, including stroke. Moderating alcohol intake is important for stroke prevention.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): AFib is a type of irregular heartbeat that can cause blood clots to form in the heart. If a blood clot travels to the brain, it can cause a stroke. Managing AFib through medication and other treatments can reduce the risk of stroke.
Stroke Prevention Strategies:
Reducing the risk of stroke involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and ongoing monitoring. Strategies for stroke prevention include:
- Monitor Blood Pressure: Regularly monitor blood pressure and work with a healthcare professional to keep it within a healthy range through lifestyle changes and medication if necessary.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit sodium, saturated fats, and added sugars, which can contribute to high blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Engage in Regular Physical Activity: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise each week. Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight, lower blood pressure, and improve overall cardiovascular health.
- Quit Smoking: If you smoke, seek support and resources to quit smoking. Quitting smoking significantly reduces the risk of stroke and improves overall health.
- Manage Diabetes: Work with your healthcare provider to manage diabetes through medication, monitoring blood sugar levels, and adopting a healthy lifestyle.
- Control Cholesterol Levels: Maintain healthy cholesterol levels through diet, exercise, and medication if prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Limit Alcohol Intake: If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. Limit your intake as much as possible.
Stroke prevention is achievable through a combination of lifestyle modifications, medical interventions, and ongoing management of risk factors. By understanding the risk factors for stroke and adopting healthier habits, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of experiencing a stroke and improve their overall quality of life. It’s important to
work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized prevention plan tailored to individual needs and circumstances. By prioritizing stroke prevention, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their brain health and well-being.